ABA routing numbers play a crucial role in facilitating seamless financial transactions across the United States. As the backbone of the banking system, these unique nine-digit codes ensure accurate movement of funds between financial institutions. Whether you're setting up direct deposits, paying bills online, or transferring money, understanding ABA routing numbers is essential for managing your finances effectively.
In today's digital age, where financial transactions happen at the speed of light, the importance of ABA routing numbers cannot be overstated. These codes serve as a digital address, ensuring that your money reaches the correct bank or credit union without errors. This guide will delve into the intricacies of ABA routing numbers, explaining their structure, purpose, and how they function in various banking operations.
Whether you're a personal account holder or a business owner, having a clear understanding of ABA routing numbers can help you avoid common banking mistakes and streamline your financial processes. This article will provide you with all the information you need to navigate the world of ABA routing numbers confidently.
Read also:When Did Angie Dickinson Pass Away A Comprehensive Look At Her Life And Legacy
Table of Contents
- What is an ABA Routing Number?
- History of ABA Routing Numbers
- Structure of an ABA Routing Number
- Types of ABA Routing Numbers
- How to Find Your ABA Routing Number
- Common Uses of ABA Routing Numbers
- ABA vs. SWIFT vs. IBAN
- Security Measures for ABA Routing Numbers
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- The Future of ABA Routing Numbers
What is an ABA Routing Number?
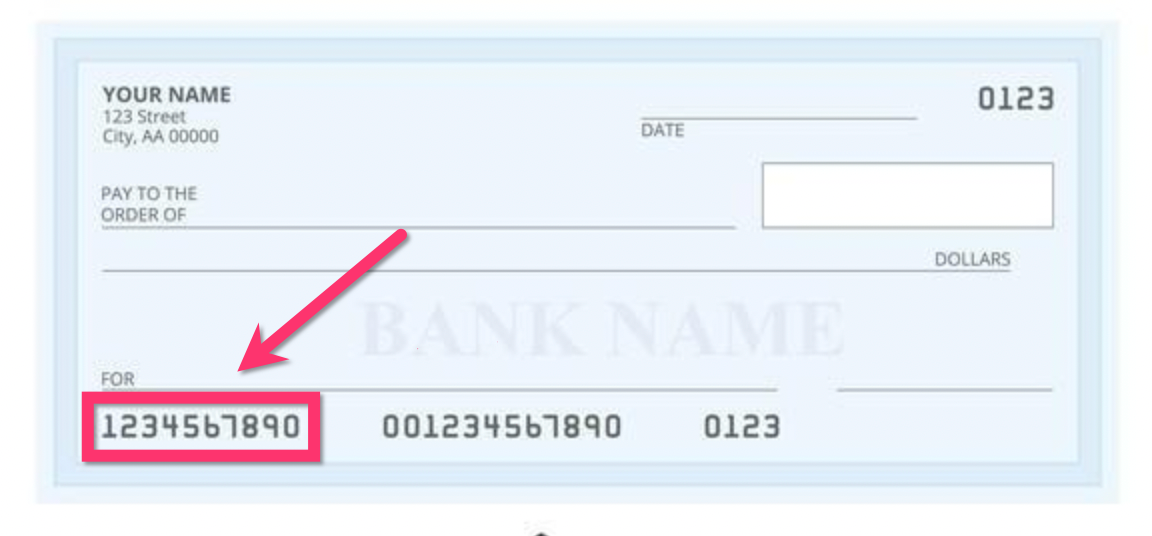
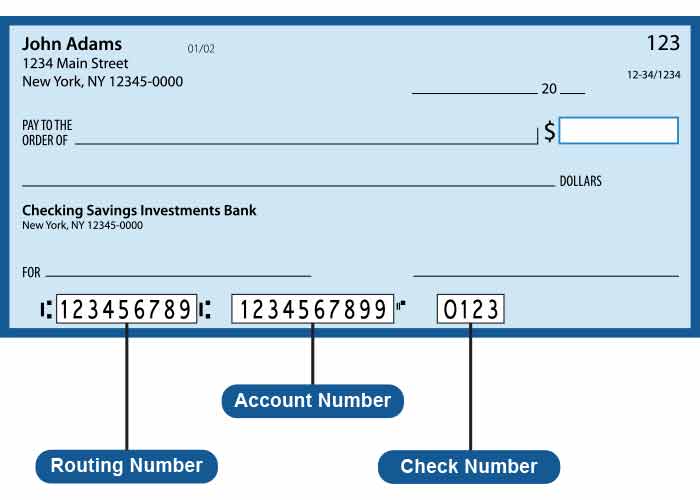
An ABA routing number, also known as a routing transit number (RTN), is a nine-digit code used by financial institutions in the United States to identify the specific bank or credit union involved in a transaction. This number ensures that funds are directed to the correct institution, whether for wire transfers, direct deposits, or check processing.
ABA routing numbers are essential for domestic transactions within the U.S. and are used by both individuals and businesses. Each financial institution has its unique routing number, which is assigned based on its location and membership in the American Bankers Association (ABA).
For example, if you're setting up a direct deposit for your salary, your employer will require your bank account number and ABA routing number to ensure the funds are deposited into the correct account.
History of ABA Routing Numbers
Origins and Evolution
The ABA routing number system was first introduced in 1910 by the American Bankers Association to standardize check processing. Initially designed to simplify the manual sorting of checks, the system has evolved to accommodate modern electronic banking transactions.
Today, ABA routing numbers are managed by Accuity, a global provider of regulatory and financial data solutions. Accuity ensures the accuracy and integrity of routing numbers, updating them regularly to reflect changes in the banking landscape.
- 1910: Introduction of ABA routing numbers
- 1940s: Expansion to include electronic transactions
- 2000s: Integration with modern banking systems
Structure of an ABA Routing Number
Breaking Down the Nine-Digit Code
An ABA routing number consists of nine digits, each with a specific purpose:
Read also:Manchester United Vs Liverpool The Epic Football Rivalries
- Digits 1-4: Federal Reserve Routing Symbol
- Digits 5-8: Institution Identifier
- Digit 9: Check Digit
The check digit is a mathematical calculation used to verify the accuracy of the routing number. This ensures that any errors in transcription or data entry can be quickly identified and corrected.
Types of ABA Routing Numbers
Wire Transfer vs. ACH Routing Numbers
It's important to note that some banks have different routing numbers for different types of transactions:
- Wire Transfer Routing Numbers: Used for real-time, high-priority transactions.
- ACH Routing Numbers: Used for automated clearing house transactions, such as direct deposits and bill payments.
Always confirm with your bank which routing number to use for your specific transaction type to avoid delays or errors.
How to Find Your ABA Routing Number
Methods for Locating Your Routing Number
There are several ways to find your ABA routing number:
- Check: The routing number is located at the bottom left corner of your personal or business checks.
- Bank Statement: Your routing number is often listed on your monthly bank statement.
- Online Banking: Most banks provide your routing number through their online banking portals.
- Bank's Website: Many financial institutions publish their routing numbers on their official websites.
For example, if you're a customer of Bank of America, you can find your routing number by visiting their website and entering your account details.
Common Uses of ABA Routing Numbers
Key Applications in Banking
ABA routing numbers are used in various banking operations, including:
- Direct Deposits: Ensuring your salary or benefits are deposited directly into your account.
- Bill Payments: Facilitating automatic payments for utilities, loans, and other recurring expenses.
- Wire Transfers: Sending or receiving large sums of money domestically or internationally.
- Check Processing: Verifying the authenticity and routing of checks.
Understanding these applications can help you manage your finances more efficiently and avoid potential errors.
ABA vs. SWIFT vs. IBAN
Comparing Domestic and International Banking Codes
While ABA routing numbers are used for domestic transactions in the U.S., other codes are used for international transactions:
- SWIFT Codes: Used for international wire transfers, identifying banks globally.
- IBAN Codes: Used for international bank account identification, ensuring accurate cross-border transactions.
For example, if you're sending money from the U.S. to Europe, you'll need both an ABA routing number and a SWIFT code to complete the transaction.
Security Measures for ABA Routing Numbers
Protecting Your Financial Information
It's crucial to safeguard your ABA routing number to prevent unauthorized access to your account. Here are some security tips:
- Keep Your Checks Secure: Avoid leaving checks unattended or in insecure locations.
- Monitor Your Account: Regularly review your bank statements for any suspicious activity.
- Use Secure Connections: Always access your online banking through secure, encrypted connections.
By following these best practices, you can help protect your financial information and prevent fraud.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Resolving Routing Number Problems
Common issues with ABA routing numbers include:
- Incorrect Number: Double-check the routing number to ensure accuracy.
- Transaction Delays: Verify that the correct routing number and account number are provided.
- Bank Changes: Confirm with your bank if there have been any updates to your routing number.
If you encounter any issues, contact your bank's customer service for assistance.
The Future of ABA Routing Numbers
Adapting to Modern Banking Needs
As technology continues to evolve, ABA routing numbers will likely adapt to meet the changing needs of the banking industry. Innovations such as real-time payments and blockchain technology may influence how routing numbers are used in the future.
For now, ABA routing numbers remain a vital component of the U.S. banking system, ensuring the smooth flow of funds across the country.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding ABA routing numbers is essential for managing your finances effectively. From facilitating direct deposits to ensuring accurate check processing, these nine-digit codes play a critical role in the U.S. banking system. By familiarizing yourself with their structure, uses, and security measures, you can avoid common banking pitfalls and streamline your financial operations.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information. Feel free to leave a comment below with any questions or insights you may have. For more informative content on personal finance and banking, explore our other articles on the website.