Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) plays a pivotal role in shaping the financial reporting landscape in the United States. It serves as the primary authority responsible for establishing accounting standards that guide businesses and organizations in preparing their financial statements. In an era where transparency and accountability are paramount, understanding FASB's role and its standards is crucial for anyone involved in finance, accounting, or business management.
FASB operates under the auspices of the Financial Accounting Foundation (FAF) and is dedicated to improving financial accounting and reporting standards. By setting guidelines that ensure consistency and reliability in financial reporting, FASB contributes significantly to maintaining trust in the financial markets. Its efforts help investors, regulators, and other stakeholders make informed decisions based on accurate and transparent financial information.
This article delves into the intricacies of FASB, exploring its history, functions, key standards, and the impact it has on businesses and the economy. Whether you're a seasoned accountant, a finance professional, or simply curious about how financial standards are developed, this guide offers valuable insights into the workings of the Financial Accounting Standards Board.
Read also:Hilton Garden Inn Providence A Premier Destination For Your Rhode Island Getaway
Table of Contents
- The History of Financial Accounting Standards Board
- Structure and Governance of FASB
- Key Financial Accounting Standards
- The Standard-Setting Process
- Impact of FASB Standards on Businesses
- Challenges Faced by FASB
- FASB's Role in Global Accounting Standards
- The Future of Financial Accounting Standards
- Benefits of FASB Standards
- Conclusion and Next Steps
The History of Financial Accounting Standards Board
Established in 1973, the Financial Accounting Standards Board was created to address the growing need for standardized financial reporting practices in the United States. Prior to its formation, accounting standards were developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) through its Committee on Accounting Procedure (CAP). However, the increasing complexity of financial transactions and the need for more comprehensive standards necessitated the establishment of a dedicated body.
FASB's creation marked a significant shift in the approach to financial standard-setting. It introduced a more structured and transparent process for developing and implementing accounting standards. Over the years, FASB has evolved to meet the changing needs of the financial landscape, adapting its standards to reflect advancements in technology, business practices, and global economic trends.
Key Milestones in FASB's History
- 1973: Formation of FASB as an independent standard-setting body.
- 1984: Introduction of the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 95, mandating cash flow statements.
- 2008: Release of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification, simplifying access to all authoritative U.S. GAAP standards.
- 2016: Adoption of the Current Expected Credit Loss (CECL) model, enhancing credit loss reporting.
Structure and Governance of FASB
FASB operates under the oversight of the Financial Accounting Foundation (FAF), which ensures its independence and impartiality. The board consists of seven full-time members, each bringing a wealth of expertise in accounting, auditing, and finance. Members are appointed by the FAF Board of Trustees after a rigorous selection process to ensure a diverse range of perspectives and experiences.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
- Chairman: Leads the board and oversees the standard-setting process.
- Board Members: Contribute to the development and approval of accounting standards.
- Technical Staff: Provides research and analysis to support the board's decision-making.
FASB's governance structure is designed to promote transparency and accountability. It engages with stakeholders through public consultations, roundtables, and comment letters, ensuring that its standards reflect the needs and concerns of the broader financial community.
Key Financial Accounting Standards
One of the primary functions of FASB is to establish and maintain accounting standards that govern financial reporting. These standards, collectively known as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), provide a framework for preparing and presenting financial statements. Below are some of the key standards developed by FASB:
Revenue Recognition Standards
The revenue recognition standard, codified as ASC 606, outlines the principles for recognizing revenue in financial statements. It emphasizes the importance of identifying performance obligations, determining transaction prices, and allocating revenue to specific obligations.
Read also:When Is Madden 24 Come Out Your Ultimate Guide To The Upcoming Football Game
Lease Accounting Standards
FASB's lease accounting standard, ASC 842, requires organizations to recognize lease liabilities and corresponding right-of-use assets on their balance sheets. This standard aims to improve transparency in financial reporting by providing a clearer picture of an entity's leasing activities.
Financial Instruments Standards
The financial instruments standard addresses the classification, measurement, and disclosure requirements for financial assets and liabilities. It ensures consistency in reporting financial instruments, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions based on accurate financial data.
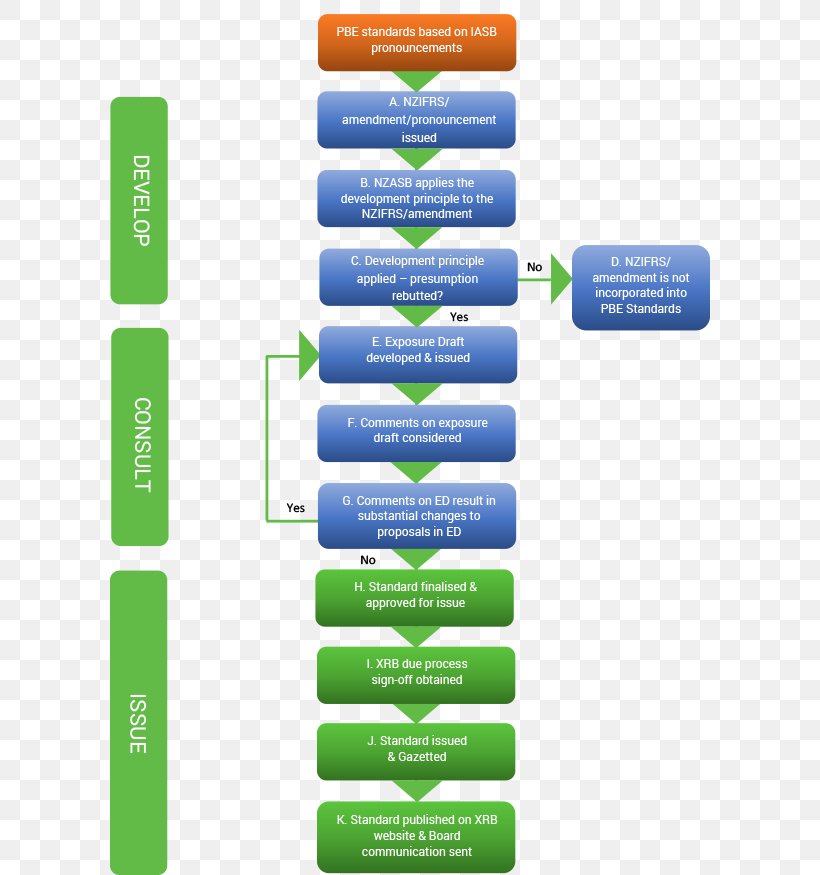
The Standard-Setting Process
FASB follows a rigorous and transparent process for developing and implementing accounting standards. This process involves several stages, each designed to ensure that the standards are well-researched, thoroughly vetted, and aligned with the needs of the financial community.
Stages of the Standard-Setting Process
- Agenda Request: Stakeholders submit requests for topics to be added to FASB's agenda.
- Research and Analysis: FASB's technical staff conducts research and analysis to understand the issues and potential solutions.
- Public Consultation: Draft proposals are released for public comment, allowing stakeholders to provide feedback.
- Board Deliberation: The board reviews feedback and refines the proposal based on input received.
- Final Standard: After final approval, the standard is issued and becomes part of U.S. GAAP.
Impact of FASB Standards on Businesses
FASB's standards have a profound impact on businesses across all industries. By promoting consistency and transparency in financial reporting, these standards help organizations build trust with investors, regulators, and other stakeholders. Companies that adhere to FASB standards can enhance their reputation, reduce the risk of non-compliance, and improve their overall financial performance.
Benefits for Businesses
- Improved financial transparency and accountability.
- Enhanced investor confidence and trust.
- Streamlined compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Increased efficiency in financial reporting processes.
However, implementing FASB standards can also present challenges, particularly for smaller organizations with limited resources. Businesses must invest time and effort in understanding and adopting these standards to ensure compliance and maximize their benefits.
Challenges Faced by FASB
Despite its many successes, FASB faces several challenges in its mission to develop and maintain high-quality accounting standards. These challenges include:
Globalization and Cross-Border Reporting
As businesses increasingly operate across borders, FASB must address the complexities of international financial reporting. Harmonizing U.S. GAAP with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) remains a significant challenge, requiring ongoing collaboration with global standard-setting bodies.
Technological Advancements
Rapid advancements in technology have introduced new accounting issues, such as the treatment of digital assets and blockchain transactions. FASB must stay ahead of these developments to ensure its standards remain relevant and effective.
Stakeholder Engagement
FASB relies heavily on input from stakeholders to inform its standard-setting process. However, balancing the diverse needs and perspectives of various groups can be challenging, requiring careful consideration and compromise.
FASB's Role in Global Accounting Standards
FASB plays a critical role in shaping global accounting standards through its collaboration with the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). While U.S. GAAP and IFRS differ in some respects, FASB and IASB work together to converge their standards where possible, promoting consistency and comparability in financial reporting worldwide.
Key Areas of Collaboration
- Revenue recognition standards.
- Lease accounting standards.
- Financial instruments standards.
This collaboration benefits businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions by reducing the burden of complying with differing accounting standards and enhancing the comparability of financial statements across borders.
The Future of Financial Accounting Standards
Looking ahead, FASB will continue to evolve in response to changing economic, technological, and regulatory environments. Key areas of focus for the future include:
Sustainability and Environmental Reporting
As environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues gain prominence, FASB may explore ways to incorporate sustainability reporting into its standards. This could involve developing guidelines for measuring and disclosing environmental impacts, contributing to more holistic financial reporting.
Emerging Technologies
FASB will need to address the accounting implications of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT). By staying ahead of these trends, FASB can ensure its standards remain relevant and effective in the digital age.
Benefits of FASB Standards
The adoption of FASB standards offers numerous benefits to businesses, investors, and the broader financial community. These benefits include:
Enhanced Transparency
FASB standards promote transparency in financial reporting, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions based on accurate and reliable information.
Increased Accountability
By establishing clear guidelines for financial reporting, FASB helps organizations maintain accountability and adhere to ethical practices.
Improved Investor Confidence
Investors can trust financial statements prepared in accordance with FASB standards, leading to increased confidence and willingness to invest in businesses.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the Financial Accounting Standards Board plays a vital role in shaping the financial reporting landscape in the United States. Through its commitment to developing high-quality accounting standards, FASB ensures consistency, transparency, and accountability in financial reporting. Businesses that embrace FASB standards can enhance their reputation, reduce risks, and improve their overall financial performance.
We encourage readers to engage with FASB by providing feedback on proposed standards and participating in public consultations. By doing so, you can help shape the future of financial accounting and reporting. Share this article with your colleagues and explore other resources on our website to deepen your understanding of financial standards and practices.